- Hepasim®:Active compound of ACM ( cinnamomea mycelia)
Simpson Biotech has developed a proprietary sub-merged fermentation process to produce A. cinnamomea mycelia (ACM) with very high (~12%) content of active compounds Hepasim®(Antrodin A~E) protected by 37 global patents owned by Simpson Biotech. The fermentation process is well controlled for the production of consistent high quality product as dietary supplement material.
Market of natural skin lightening
Skin lightening or whitening cosmetics reduce the melanin accumulation in the skin. Skin-whitening products are particularly popular in Asian (India, China, Japan, and Korea). In fact, with a naturally higher skin hydration level, Asian skin is particularly prone to suffer from hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation disorders, and to display general unevenness of skin tone with age rather than to wrinkle.
Numerous chemical substances have already been proven as effective skin whiteners, and even display beneficial side effects (antioxidants are effective against UV radiation). Some chemical substances, however, have recently raised safety concerns, leading to bans in many countries. Due to consumers’ concern about synthetic ingredients and their potential risk for human health, cosmetic producers have searched for non-cytotoxic natural whitening ingredients from natural materials in recent years.
Hepasim® has strong skin lightening efficacy with high safety profile
- Extracted from very safe natural biomaterial
- Inhibition of melanin accumulation under 10 ppm
- Better efficacy than common natural compounds
- Novel working mechanism
- Anti-oxidation activity
- Anti-scar activity
- High bioavailability
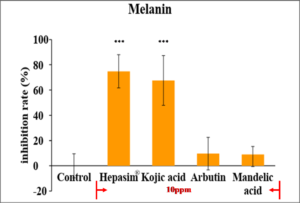
As a natural extracted ingredient, Hepasim® can efficiently reduce melanin accumulation in human cells. With extremely low cytotoxity, Hepasim® treatment (10 ppm) could inhibit almost 80% melanin induced by α-MSH in B16F10 cell. This efficacy is comparable to Kojic acid, one of the most common skin whiting ingredients, and significantly better than that of Arbutin or Mandelic acid.(Fig.1)
Fig.1 Hepasim® shows better efficacy for inhibiting melanin accumulation
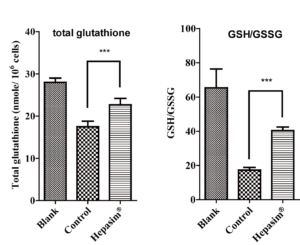
As a lipid-soluble component, Hepasim® has better skin penetration ability and formula compatibility than water-soluble components. Most skin whitening ingredients act by inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase. Interestingly, the inhibitory effect of Hepasim® to cytosolic tyrosinase activity is not such strong as Kojic acid. These results indicate that Hepasim® may inhibit melanin accumulation by other mechanisms, which leads to the further possibility that Hepasim® can be combined with other ingredients. Correlated with skin whiting, Hepasim® can also protect cells from oxidation stress by clearing free radicals. Glutathione level and GSH:GSSG ratio as markers for oxidative stress, is significantly improved in cells treated with Hepasim® compared to those in the H2O2-treated control cells (Fig.2).
Fig.2 Hepasim® can protect cells from oxidation stress by clearing free radicals.
Besides skin whiting, Hepasim® also has anti-scar activity. Topical application (1% w/v) of Hepasim® (and Antrodin) could reduce 42% of scar thickness in animal models (Fig.3).
